When working with fasteners, it’s easy to overlook the role of a small, flat disc called the washer. Yet, washers are crucial in ensuring a screw holds materials together securely and lasts over time. If you’ve ever asked yourself how to use washers with screws properly, this guide will walk you through the process in detail—drawing from real-world experience in fastening applications.
Why Use Washers with Screws?
At their core, washers do two important jobs:
- Distribute load – A washer spreads the pressure of the screw head across a larger area. This prevents dents, cracks, or warping, especially in softer materials like wood or plastic.
- Provide stability – Washers give screws a smooth, even surface to tighten against. This reduces loosening from vibration and helps maintain a solid joint over time.
Simply put, washers make screw connections stronger, cleaner, and more durable.

Common Types of Washers
Not all washers are the same. Choosing the right type depends on your project:
- Flat Washers – The most versatile type. They provide general load distribution and surface protection.
- Lock Washers – Designed to resist loosening caused by vibration. Ideal for machinery, vehicles, or any assembly under constant movement.
- Split Washers (Spring Washers) – Apply tension that helps screws stay in place. Useful when fastening into thin or flexible materials.
Common Types of Screws
Since washers are always paired with screws, it’s important to understand which screw type you’re working with:
Self-Tapping Screws – Cut their own threads as they’re driven in.
Wood Screws – Coarse threads and tapered shanks for gripping wood.
Machine Screws – Fine-threaded screws for metal-to-metal fastening.
Sheet Metal Screws – Sharp points for fastening thin metal or plastic sheets.

You may also want to learn about structural screws and concrete screws.
How to Use Washers with Screws (Step by Step)
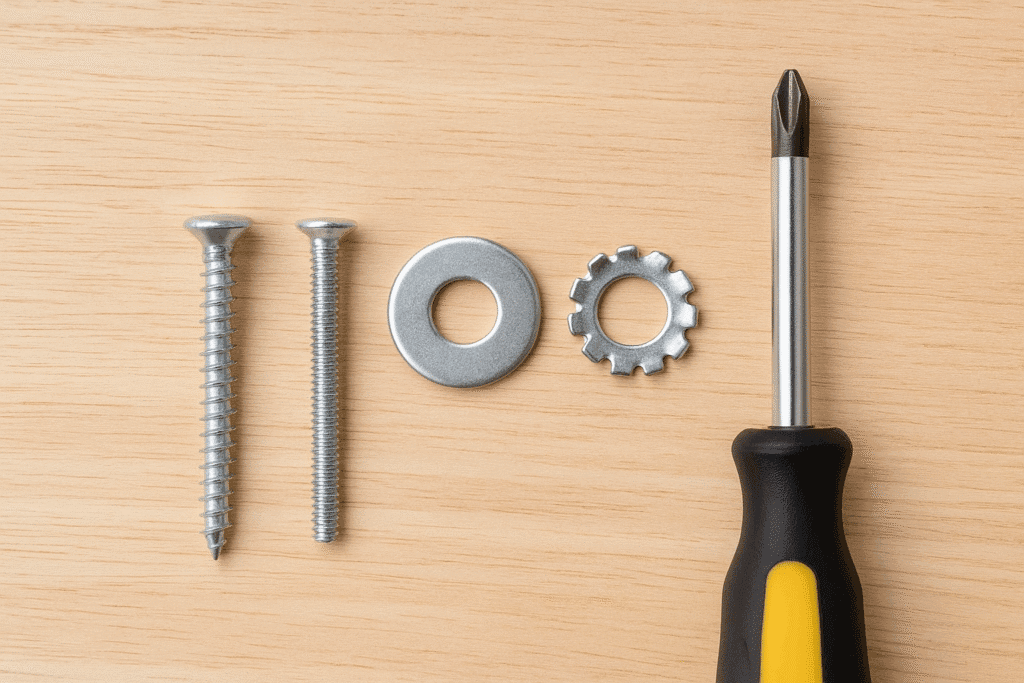
Here’s the process I recommend for securing washers with screws:
- Select the right parts
Choose a washer and screw type that match your material and load requirements. For example, use a lock washer with machine screws in vibrating equipment, or a flat washer with wood screws to protect the surface. - Prepare the material
Ensure the surface is clean. If needed, pre-drill a pilot hole—especially in hardwoods or metal—to avoid splitting or stripping. - Align the washer
Place the washer flat against the surface, with its hole centred over the screw location. Misalignment reduces load distribution and weakens the joint. - Insert the screw
Pass the screw through the washer and into the material. Make sure the washer doesn’t shift out of place. - Tighten carefully
Drive the screw until it’s snug against the washer. Avoid overtightening—this can deform the washer, strip threads, or crack the material. A good rule is “tight, but not forced.”
Benefits of Using Washers with Screws
- Secure fastening – Washers reduce loosening over time.
- Protect materials – They prevent dents, cracks, and warping.
- Stronger joints – The added surface area increases holding power.
- Cost-effective durability – Washers are inexpensive but extend the life of your fastened connections.
Tips from a Fastener Expert
- Always match the washer size to the screw diameter. A washer that’s too large or too small won’t distribute force properly.
- For projects exposed to weather, use stainless steel washers to prevent rust.
- In high-vibration settings, pair a lock washer with thread-locking fluid for maximum security.
- If you’re fastening into very thick material, consider stacking washers to distribute the load further.
Removing Washers and Screws
Taking them out is usually straightforward:
- Use the correct screwdriver to avoid stripping.
- Turn slowly and evenly until the screw releases.
- If stuck, apply penetrating oil and let it soak before trying again.
- Keep the washer and screw if they’re still in good condition—they’re often reusable.
Mistakes to Avoid
- Wrong fastener choice – Using the wrong type of screw or washer weakens the joint.
- Misalignment – A washer that isn’t flat against the surface won’t do its job.
- Overtightening – Damages both washer and material.
- Undertightening – Leaves the joint loose and unstable.
You may also want to read about how to measure screw size.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do you put the washer before the screw?
Yes, the washer should go before the screw head—meaning you slide the washer onto the screw before driving it into the material. This positioning allows the washer to distribute the load and protect the surface as soon as the screw engages.
Can you use washers with wood screws?
Absolutely. Using a washer with a wood screw helps spread the pressure ovAbsolutely. Using a washer with a wood screw helps spread the pressure over a larger area, reducing the risk of the screw head sinking into soft materials like wood.
That said, experienced woodworkers often countersink the screw head into the wood, making a washer unnecessary—especially when working with fine hardwood joinery. Reddit
When should you use a washer—and when should you skip it?
Here are some quick guidelines:
Use a washer when:
You need to distribute the load to prevent damage to soft or delicate materials.
You want to protect the surface from scratching or denting.
The joint may experience vibration or movement—using a lock or spring washer helps maintain tension.
You’re dealing with sealing or spacing needs—e.g., distributing pressure over a gasket or creating a gap.
Skip the washer when:
The materials and fastener surfaces are already uniform and secure, with low risk of damage.
The fastener has a built-in large bearing surface, like a flange head, offering built-in load distribution.
Space is extremely limited and adding a washer would hinder fit or function.
Where does a washer go when using a bolt and nut assembly?
If using just one washer, a common practice is to place it on the nut side. This is because the nut is often the moving part, and the washer helps protect the surface as it’s tightened.
That said, there’s room for logic and practical adjustment:
Flat and load-distributing washers can go under the part you’re protecting—be it bolt head or nut—as needed.
Lock washers should typically sit under the nut to resist loosening from vibration.
Can washers help protect surfaces from corrosion or wear?
Yes. Washers—especially ones made from the right material—can prevent galvanic corrosion, such as when steel fasteners contact aluminum surfaces. They act as insulation barriers.
Additionally, hardened washers help prevent wear (brinelling) by distributing torque more evenly. Wikipedia
As a fastener expert, any quick tips on placing washers with screws?
Match washer size to screw diameter for optimal surface load distribution.
In outdoor or wet conditions, use stainless or coated washers to prevent rust.
For high-vibration situations, pair a lock washer with thread-locking compound for extra security.
When fastening thick materials, stack washers if needed to evenly distribute pressure.
For gasketed or sealed joints, washers ensure uniform pressure and a durable seal.
Final Thoughts
Knowing how to use washers with screws properly can make the difference between a weak joint and a long-lasting connection. By choosing the right parts, aligning them carefully, and tightening with precision, you’ll ensure your projects are secure, durable, and professional-looking.
Whether you’re tackling a DIY project at home or assembling industrial machinery, washers are more than just small accessories—they’re essential to strong, reliable fastening.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. Always consult with a licensed contractor or construction professional for your specific needs.



1 Comment